Purpose
Pulmonary function tests can help a doctor diagnose a range of respiratory diseases which might not otherwise be obvious to the doctor or the patient. The tests are important since many kinds of lung problems can be successfully treated if detected early.
The tests are also used to measure how a lung disease is progressing, and how serious the lung disease has become. Pulmonary function tests also can be used to assess how a patient is responding to different treatments.
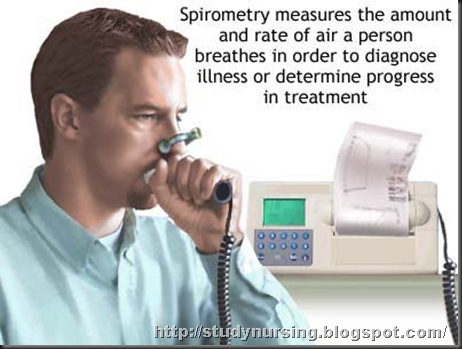 One of the most common of the pulmonary function tests is spirometry (from the Greco-Latin term meaning "to measure breathing"). This test, which can be given in a hospital or doctor's office, measures how much and how fast the air is moving in and out of the lungs. Specific measurements taken during the test include the volume of air from start to finish, the fastest flow that is
One of the most common of the pulmonary function tests is spirometry (from the Greco-Latin term meaning "to measure breathing"). This test, which can be given in a hospital or doctor's office, measures how much and how fast the air is moving in and out of the lungs. Specific measurements taken during the test include the volume of air from start to finish, the fastest flow that is
achieved, and the volume of air exhaled in the first second of the test.
A peak flow meter can determine how much a patient's airways have narrowed. A test of blood gases is a measurement of the concentration of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the blood, which shows how efficient the gas exchange is in the lungs.
Another lung function test reveals how efficient the lungs are in absorbing gas from the blood. This is measured by testing the volume of carbon monoxide a person breathes out after a known volume of the gas has been inhaled.
Pulmonary function tests shouldn't be given to patients who have had a recent heart attack, or who have certain other types of heart disease. It is crucial that the patient cooperate with the health care team if accurate results are to be obtained.
Description
The patient places a clip over the nose and breathes through the mouth into a tube connected to a machine known as a spirometer. First the patient breathes in deeply, and then exhales as quickly and forcefully as possible into the tube. The exhale must last at least six seconds for the machine to work properly. Usually the patient repeats this test three times, and the best of the three results is considered to be the measure of the lung function. The results will help a doctor figure out which type of treatment to pursue.
Pulmonary function tests are a group of procedures that measure the function of the lungs, revealing problems in the way a patient breathes. The tests can determine the cause of shortness of breath and may help confirm lung diseases, such as asthma, bronchitis or emphysema. The tests also are performed before any major lung surgery to make sure the person won't be disabled by having a reduced lung capacity.
Preparation
The patient should not eat a heavy meal before the test, nor smoke for four to six hours beforehand. The patient's doctor will issue specific instructions about whether or not to use specific medications, including bronchodilators or inhalers, before the test. Sometimes, medication may be administered as part of the test.
Risks
The risk is minimal for most people, although the test carries a slight risk of a collapsed lung in some patients with lung disease.
Normal results
Normal results are based on a person's age, height, and gender. Normal results are expressed as a percentage of the predicted lung capacity. The prediction takes into account the patient's age, height, and sex.
Abnormal results
Abnormal results mean that the person's lung capacity is less than 80% of the predicted value. Such findings usually mean that there is some degree of chest or lung disease.
Spirometry is a painless study of air volume and flow rate within the lungs. Spirometry is frequently used to evaluate lung function in people with obstructive or restrictive lung diseases such as asthma or cystic fibrosis.
No comments:
Post a Comment